Breathing circuit
Free!
A breathing circuit is the tubing and components that link a patient to an anesthesia machine or ventilator. It delivers oxygen and anesthetic gases while directing exhaled air away to reduce CO₂ rebreathing. Choose circle systems for gas efficiency and humidity retention, or non-rebreathing sets for lightweight simplicity during transport. Built for compatibility with common connectors and filters, it supports safe, reliable ventilation in OR, ICU, and emergency settings.
Description
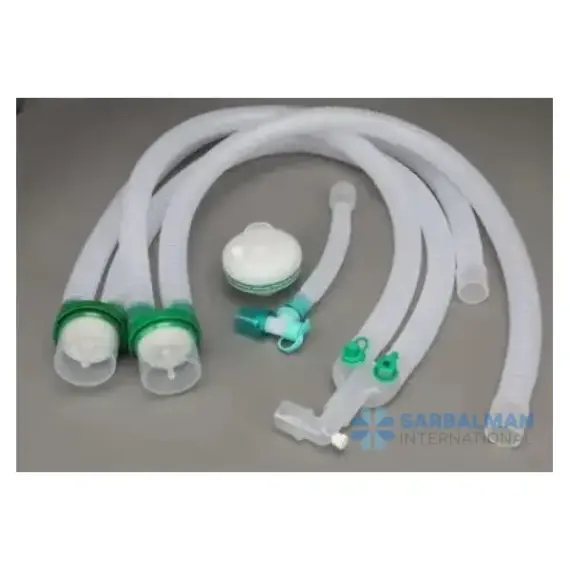
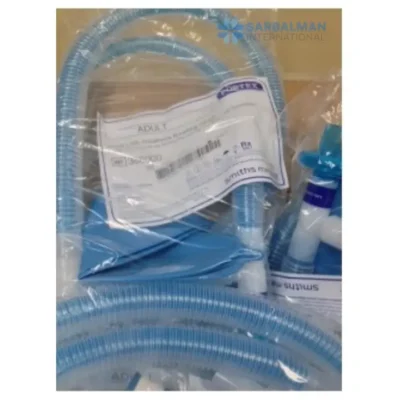
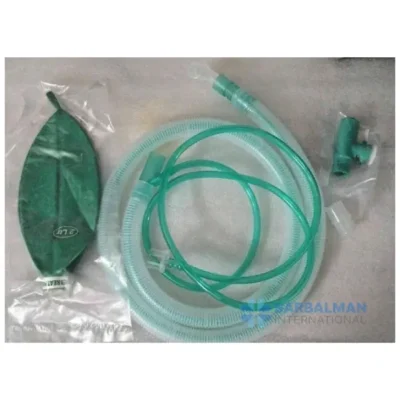
A breathing circuit is a complete gas pathway that connects a patient to an anesthesia machine or ventilator. It delivers oxygen and anesthetic gases during procedures or assisted ventilation while directing exhaled air away and helping prevent carbon dioxide rebreathing. Typical components include corrugated tubing, a Y-piece or single-limb connector, a reservoir bag, and a pressure-relief valve. Circuits are broadly of two types: circle (rebreathing) systems that use a CO₂ absorber, and non-rebreathing systems that rely on fresh-gas flow.
Key features and benefits
• Stable ventilation with controlled flow and pressure.
• Options for circle systems to conserve heat and humidity and reduce fresh-gas consumption.
• Lightweight non-rebreathing configurations for quick setup and transport use.
• Compatible with common connectors, filters, and humidification accessories.
• Sized for neonatal, pediatric, and adult patients to reduce resistance and dead space.
Common uses and applications
• Operating rooms during general anesthesia.
• Intensive care units for short- or longer-term ventilatory support.
• Emergency and transport settings where simple, portable setups are preferred.
• Procedural sedation areas and recovery units.
Comparison and selection tips
• Circle vs non-rebreathing: circle systems improve gas economy and moisture retention; non-rebreathing systems are simpler and lighter but need higher fresh-gas flows.
• Consider patient size, ventilation mode (spontaneous vs controlled), and environment (OR, ICU, transport).
• Check for build quality, kink resistance, and compatibility with filters and sampling lines.
• Buyers often look for conformity to recognized standards for breathing sets and connectors—for example, ISO standards used in anesthesia and respiratory care.
Safety notes
• Correct sizing and assembly reduce dead space and resistance.
• Use appropriate filters and follow institutional protocols for infection control.
• Monitor capnography and pressures to detect rebreathing or obstructions early.