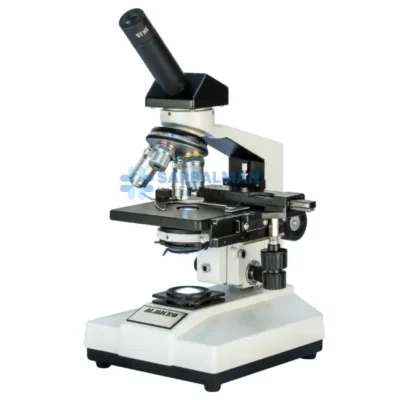
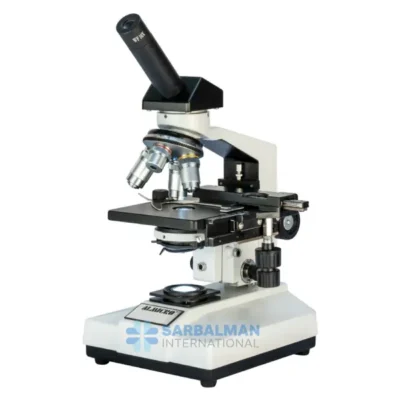
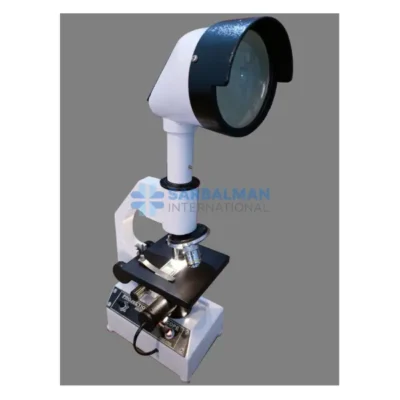
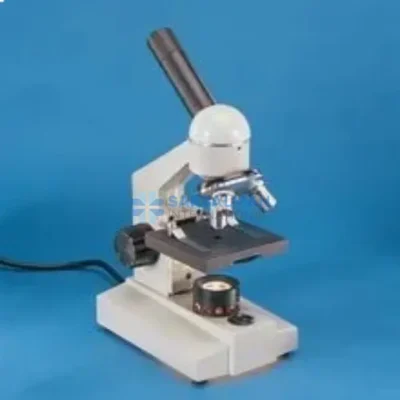
Stereoscopic Microscope
Free!
The Stereoscopic Microscope provides a crisp, 3D view of solid specimens, making it ideal for dissection, inspection, and precision work. With its low to moderate magnification, dual eyepieces, and adjustable illumination, it allows detailed observation of surfaces with depth perception. Perfect for labs, electronics, education, and crafts where visual clarity and object handling are essential.
Description
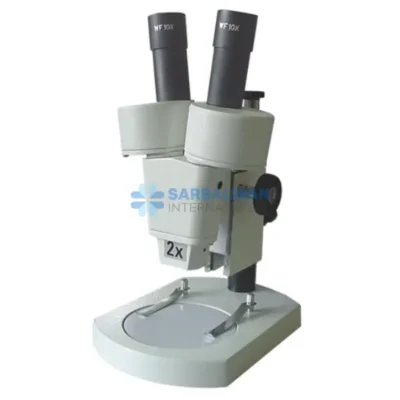
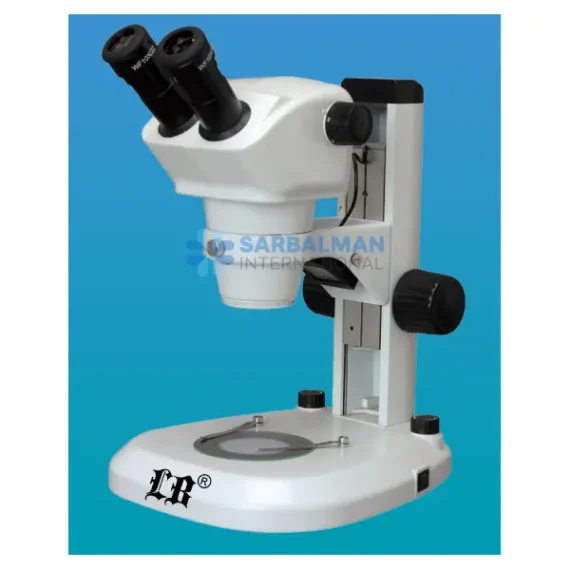
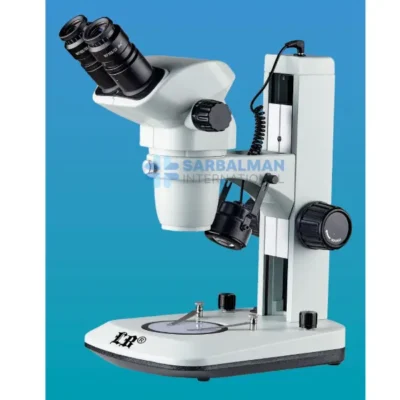
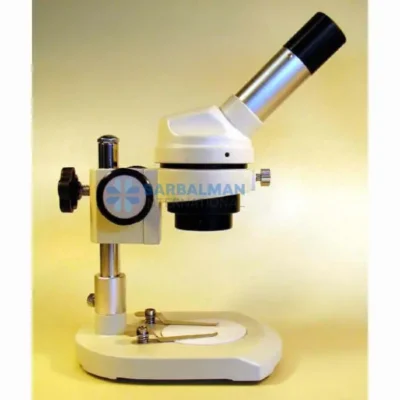
A Stereoscopic Microscope, also known as a stereo or dissecting microscope, is a low-power optical microscope that offers a three-dimensional (3D) view of a specimen. Unlike compound microscopes that provide a flat, high-magnification image of thin slices, stereoscopic microscopes are designed to observe the surface structure and detail of solid or opaque objects in real time. This makes them indispensable in fields requiring depth perception, precision handling, and visual clarity.
The stereoscopic microscope features two separate optical paths with two eyepieces and objective lenses, creating slightly different angles of the viewed object for each eye. This design mimics human binocular vision, allowing the user to perceive depth and spatial relationships—critical when manipulating small objects under the lens.
Key Features & Primary Benefits
-
True 3D Visualization
Delivers a clear, three-dimensional image of objects, ideal for studying surface textures and intricate components. -
Dual Eyepiece Viewing
Offers comfortable, fatigue-free usage even during extended sessions in labs, workshops, or classrooms. -
Low to Mid-Level Magnification
Typically ranges between 10x and 80x, optimal for dissection, assembly, inspection, and hobbyist use. -
Top and Bottom Illumination Options
Provides both reflected and transmitted light sources to suit different specimen types—transparent or solid. -
Large Working Distance
Leaves ample space between the objective lens and the specimen, making it easy to manipulate items under observation. -
User-Friendly Focus Mechanism
Smooth focus knobs and ergonomic design enable ease of use for professionals and students alike.
Common Use Cases & Applications
-
Biological dissection and botanical studies
-
Electronic circuit inspection and repair
-
Forensic sample examination
-
Gemology and mineral inspection
-
Watchmaking, coin authentication, and precision assembly
-
Educational institutions and research labs
How It Compares
While compound microscopes are suitable for observing tiny cells or microorganisms at high magnification, stereoscopic microscopes stand out in applications where depth, texture, and manipulation are key. Compared to monocular dissecting scopes, stereoscopic models offer significantly better visual depth and ease of use for detailed tasks.
Quality & Standards
Many stereoscopic microscopes conform to international optical standards and are designed with rugged durability for continuous laboratory and industrial use. Their modular configuration may support accessories such as camera attachments or zoom objectives, enhancing versatility across disciplines.